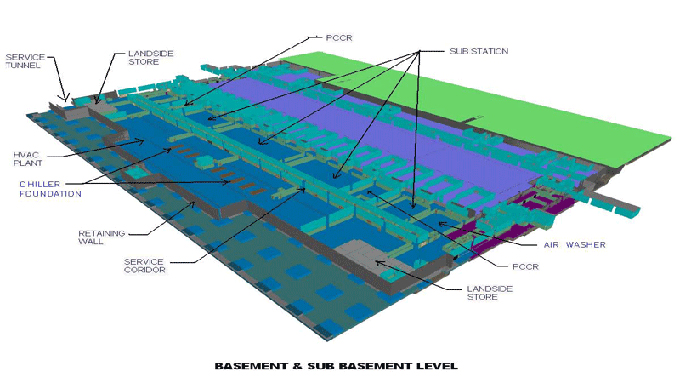
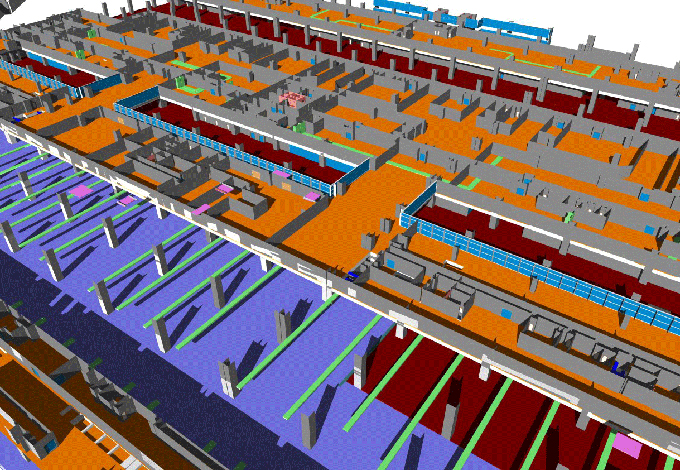
BIM for Infrastructure: Enhancing Civil Engineering Projects
Tweet
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has revolutionized the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry. While initially focused on buildings, BIM has expanded its reach to infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, and utilities. The adoption of BIM in these areas is transforming the way civil engineering projects are planned, designed, executed, and maintained.
BIM in Infrastructure Projects
The application of BIM in infrastructure projects offers numerous benefits. It facilitates better collaboration, improves accuracy, enhances visualization, and provides a comprehensive understanding of the project lifecycle. Here, we delve into how BIM is applied in various infrastructure projects.
Roads and Highways
Planning and Design
In road and highway projects, BIM aids in the creation of detailed and accurate models that incorporate topographical data, existing infrastructure, and environmental considerations. During the planning phase, BIM allows engineers to analyze different design options and assess their impact on the surrounding environment. This capability helps in optimizing routes, minimizing earthwork, and reducing environmental disruption.
The design phase benefits from BIM's ability to integrate various disciplines, such as geotechnical, structural, and drainage engineering. BIM models provide a holistic view of the project, ensuring that all aspects are considered and coordinated. This reduces the likelihood of design clashes and errors, ultimately saving time and costs.
Construction
During construction, BIM enables better project management by providing a clear visualization of the construction sequence. Construction managers can use BIM models to plan and monitor progress, identify potential issues, and mitigate risks. For instance, construction teams can simulate different scenarios to determine the most efficient construction methods, minimizing disruptions to traffic and nearby communities.
Maintenance
BIM continues to offer value post-construction by aiding in the maintenance and management of road infrastructure. Detailed as-built models serve as a reference for maintenance activities, enabling asset managers to track the condition of road elements and plan maintenance schedules effectively. This proactive approach extends the lifespan of the infrastructure and ensures safety and reliability.
Bridges
Planning and Design
BIM plays a crucial role in bridge projects by providing a detailed and accurate representation of the structure. During the planning phase, BIM allows for the analysis of different design alternatives, considering factors such as load capacity, material properties, and aesthetic considerations. This ensures that the final design meets both functional and visual requirements.
In the design phase, BIM facilitates the coordination of various disciplines involved in bridge construction, such as structural, geotechnical, and hydraulic engineering. The integration of these disciplines in a single BIM model enhances collaboration and reduces the risk of design conflicts. Additionally, BIM's 3D visualization capabilities enable stakeholders to better understand the design and provide valuable feedback.
Construction
BIM models serve as a valuable tool during the construction of bridges. Construction teams can use the models to plan construction activities, sequence tasks, and identify potential challenges. For example, BIM can simulate the construction of complex elements, such as arches or cable-stayed structures, helping engineers develop efficient and safe construction methods.
Furthermore, BIM aids in quality control by enabling the comparison of as-built conditions with the design intent. This ensures that the construction meets the specified standards and reduces the likelihood of rework.
Maintenance
Post-construction, BIM continues to provide benefits in the maintenance and management of bridges. Detailed as-built models serve as a reference for inspections and maintenance activities. Asset managers can use BIM to track the condition of bridge components, identify areas requiring maintenance, and plan repair activities. This proactive approach ensures the longevity and safety of the bridge.
Utilities
Planning and Design
In utility projects, such as water supply, sewage systems, and electrical networks, BIM aids in the planning and design phases by providing a comprehensive view of the infrastructure. Engineers can create detailed models that include information about the location of utilities, existing infrastructure, and environmental factors. This enables better coordination and reduces the risk of conflicts during construction.
During the design phase, BIM facilitates the integration of various disciplines, such as civil, mechanical, and electrical engineering. The ability to visualize the entire utility network in a single BIM model ensures that all aspects are considered and coordinated. This reduces the likelihood of design clashes and errors, ultimately saving time and costs.
Construction
During construction, BIM enables better project management by providing a clear visualization of the construction sequence. Construction managers can use BIM models to plan and monitor progress, identify potential issues, and mitigate risks. For example, BIM can simulate the installation of underground utilities, helping engineers develop efficient and safe construction methods.
Furthermore, BIM aids in quality control by enabling the comparison of as-built conditions with the design intent. This ensures that the construction meets the specified standards and reduces the likelihood of rework.
Maintenance
Post-construction, BIM continues to provide value in the maintenance and management of utility networks. Detailed as-built models serve as a reference for inspections and maintenance activities. Asset managers can use BIM to track the condition of utility components, identify areas requiring maintenance, and plan repair activities. This proactive approach ensures the longevity and reliability of the utility network.
Benefits of BIM in Infrastructure Projects
Improved Collaboration
One of the most significant benefits of BIM in infrastructure projects is improved collaboration among stakeholders. BIM provides a centralized platform where all project participants can access and share information. This ensures that everyone is working with the most up-to-date data, reducing the likelihood of errors and misunderstandings. Enhanced collaboration leads to better decision-making, increased efficiency, and improved project outcomes.
Enhanced Visualization
BIM's 3D visualization capabilities enable stakeholders to better understand the project. Visualizing the design in three dimensions provides a more realistic representation of the infrastructure, allowing stakeholders to identify potential issues early in the project lifecycle. This reduces the likelihood of costly changes and rework during construction.
Increased Accuracy
BIM improves the accuracy of project information by providing a single source of truth. The integration of various disciplines in a single BIM model ensures that all aspects of the project are considered and coordinated. This reduces the likelihood of design clashes and errors, ultimately saving time and costs.
Better Project Management
BIM enhances project management by providing a clear visualization of the construction sequence. Construction managers can use BIM models to plan and monitor progress, identify potential issues, and mitigate risks. This leads to more efficient construction processes and improved project outcomes.
Proactive Maintenance
BIM continues to provide value post-construction by aiding in the maintenance and management of infrastructure. Detailed as-built models serve as a reference for inspections and maintenance activities. Asset managers can use BIM to track the condition of infrastructure components, identify areas requiring maintenance, and plan repair activities. This proactive approach ensures the longevity and reliability of the infrastructure.
Challenges of Implementing BIM in Infrastructure Projects
While BIM offers numerous benefits, its implementation in infrastructure projects also presents challenges.
High Initial Costs
The initial costs of implementing BIM can be high, particularly for small and medium-sized firms. These costs include software licenses, hardware upgrades, and training for staff. However, the long-term benefits of BIM often outweigh the initial investment.
To get online demonstration, watch the following video tutorial.
Video Source: Federal Highway Administration USDOTFHWA
Technical Complexity
BIM involves the integration of various disciplines and requires a high level of technical expertise. This can be challenging for firms with limited experience in BIM. Investing in training and development is essential to overcome this challenge.
Resistance to Change
The adoption of BIM requires a cultural shift within organizations. Resistance to change can hinder the implementation of BIM. It is important to communicate the benefits of BIM and provide support to staff during the transition.

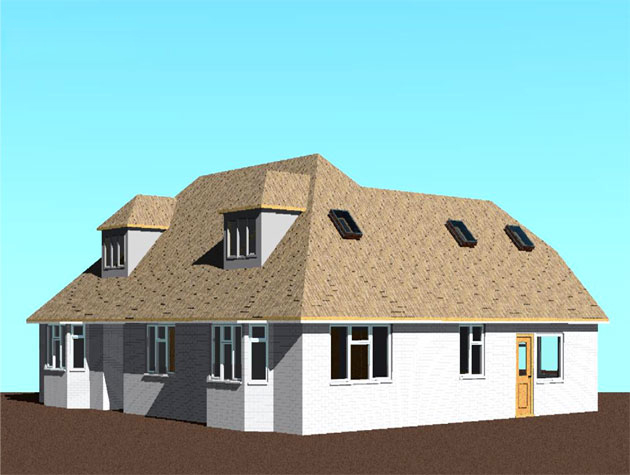
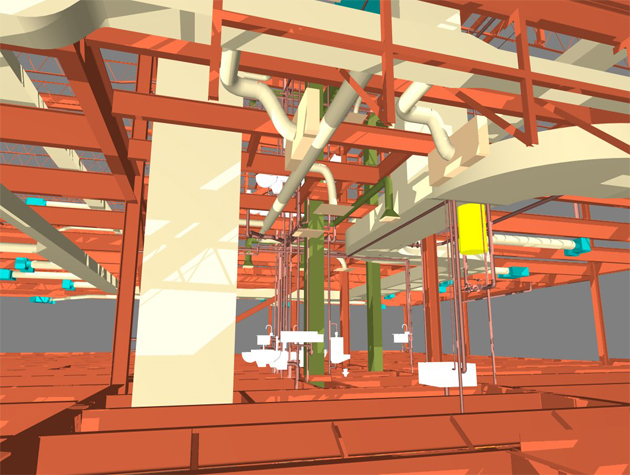
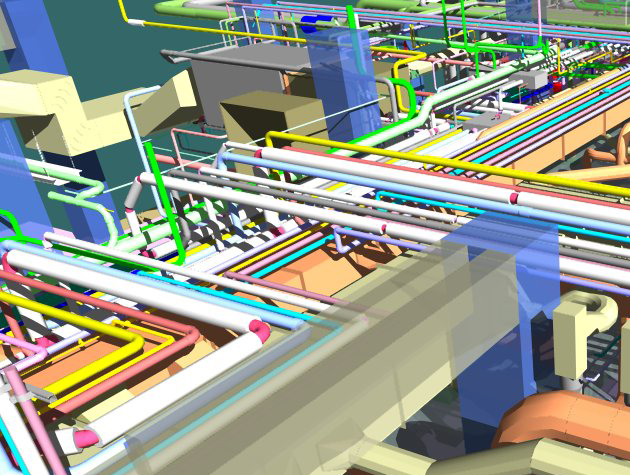
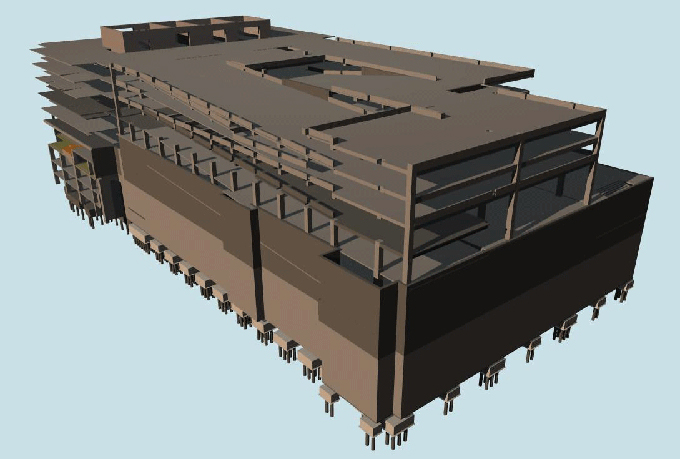
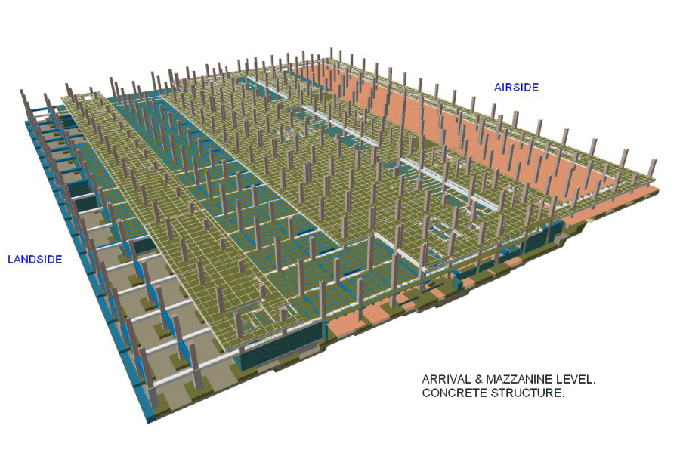
Gallery
Feel free to contact us for BIM requirements. One of our representative will respond you within 24 Hours. Send us your projects requirement today and grow your project.
Explore More !